Rational Numbers on the Number Line
Learning text on the topic Rational Numbers on the Number Line
Rational Numbers on a Number Line – Introduction
Working with rational numbers on a number line is a fundamental concept in mathematics. It enhances numerical fluency and paves the way for understanding more advanced maths topics. Rational numbers include whole numbers, fractions, and decimals, and they can be positioned on a number line that extends infinitely in both directions.
Understanding Rational Numbers – Definition
A rational number is any number that can be written as a fraction, where the top number (the numerator) and the bottom number (the denominator) are both whole numbers. Importantly, the denominator cannot be zero. The word rational comes from ratio, reflecting that these numbers represent a ratio of two quantities.
Rational numbers on a number line represent points that correspond to both whole numbers and fractions or decimals. A number line is a visual representation where these numbers are placed according to their value.
To get started, consider a number line as a horizontal line with evenly spaced divisions, each representing a unit or a fraction of a unit.
Rational Numbers on a Number Line – Example
| Step | Description | Illustration Request |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the numerator and denominator: The fraction $\frac{4}{5}$ has a numerator of 4 and a denominator of 5. The denominator tells us how many equal parts the interval from 0 to 1 is divided into. | An illustration showing a number line from 0 to 1, highlighting the concept of dividing the line based on the denominator. |
| 2 | Divide the number line: Imagine dividing the line into 5 equal sections between 0 and 1. | A detailed illustration of a number line from 0 to 1 divided into 5 equal parts, each part labelled. |
| 3 | Locate the number: Count four sections from 0. Here is where you'll place the dot for $\frac{4}{5}$. | An illustration of a number line with a dot marking the position of $\frac{4}{5}$, showing four parts from 0 highlighted or coloured differently. |
Rational Numbers on a Number Line – Guided Practice
Let's practise placing a rational number on a number line.
Rational Numbers on a Number Line – Summary
Key Learnings from this Text:
- Rational numbers include whole numbers, fractions, and decimals.
- A number line is a tool that helps visualise and understand the position and magnitude of these numbers.
- Placing a fraction on a number line involves dividing the interval into equal parts based on the denominator and locating the numeral based on the numerator.
- Comparing and ordering rational numbers is easier with a number line, as their relative positions instantly indicate their size.
- Operations like addition and subtraction of rational numbers can be visualised as movements along the number line.
- Equivalent fractions occupy the same position on a number line, reinforcing the concept of equality among different representations.
Explore other content on our platform, such as interactive practice problems and videos, to deepen your understanding of rational numbers and their placement on a number line!
Rational Numbers on a Number Line – Frequently Asked Questions

Rational Numbers on the Number Line
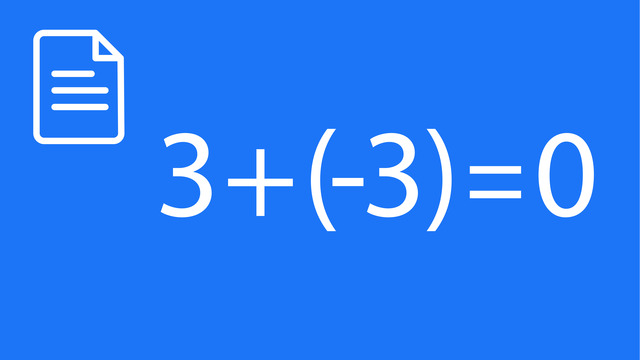
Subtracting Integers

Solving Problems with Negative Numbers
Multiplying and Dividing Integers

Rational and Irrational Numbers
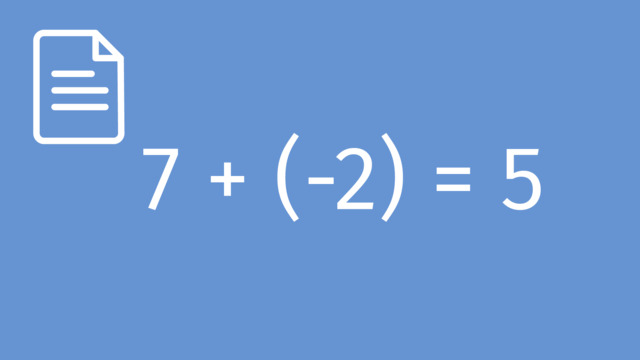
Subtracting Rational Numbers by adding the Inverse

Analysing Numerical Patterns
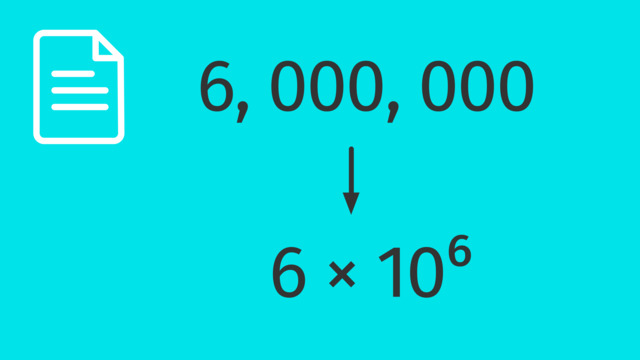
Standard and Scientific Notation
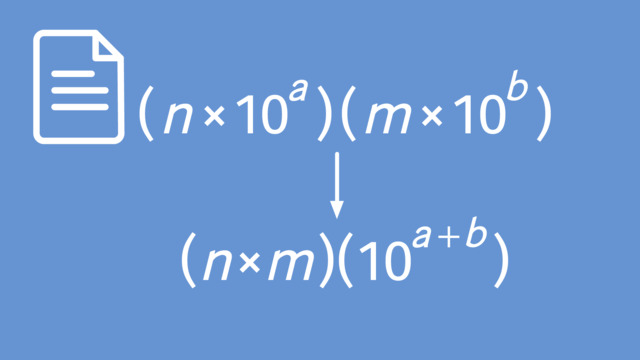
Using Operations with Scientific Notations
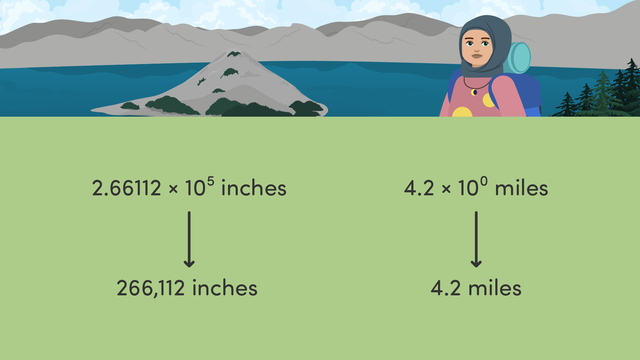
Interpreting Scientific Notation
 Do you want to learn faster and more easily?
Do you want to learn faster and more easily?






