Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem
Learning text on the topic Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem
Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry, crucial for various applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and everyday problem-solving. This theorem helps in determining the length of one side of a right triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known.
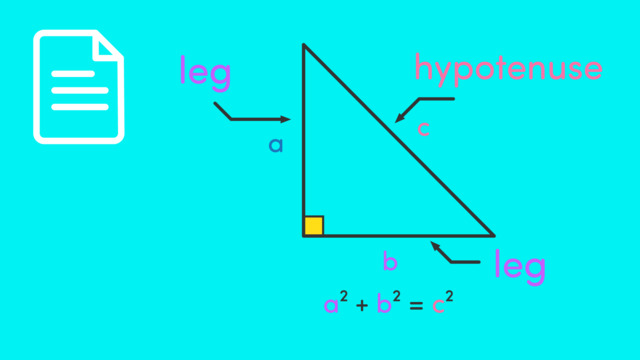
Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the longest side, always opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This relationship is expressed as $a^{2} + b^{2} = c^{2}$, where $c$ is the hypotenuse and $a$ and $b$ are the other two sides.
Understanding the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is not just a mathematical rule but a bridge to understanding spatial relationships and geometry. It provides a clear method for calculating the distance between points in a plane, an essential technique in various scientific and practical applications.
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
The beauty of the Pythagorean Theorem lies in its proof, which combines simple geometry with algebraic manipulation. Here’s how it’s typically proven:
| Step | Description | Example | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct a right triangle | Draw a triangle with sides of lengths 3, 4, and 5 | |
| 2. | Draw squares on each side | Create squares on each side of the triangle | |
| 3. | Calculate the area of each square | Find the area of each square using side lengths | |
| 4. | Show that the areas add up | Prove that the sum of the areas equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse |
Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem – Practice
Let’s work through the following problem together to apply the Pythagorean Theorem:
Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem – Summary
Key Learnings from this Text:
- The Pythagorean Theorem describes a fundamental relationship in right triangles.
- It is expressed as $a^{2} + b^{2} = c^{2}$, where $c$ is the hypotenuse.
- The theorem is not only theoretical but also practical, used in various real-world applications.
 Do you want to learn faster and more easily?
Do you want to learn faster and more easily?